Image optimization seo best practices
Image optimization SEO is one of the more often overlooked elements of on-page SEO, but that doesn’t mean it’s not important. In fact, if you’re not careful, poor image SEO can do a heck of a job of sinking your page’s ability to gain links, rise in the index, and, ultimately, drive valuable organic traffic.
What is Image optimization in SEO?
Visual content plays a pivotal role in engaging online audiences, mastering the art of Image SEO (Search Engine Optimization) has become essential for achieving optimal search visibility. Properly optimized images not only enhance user experience but also contribute to higher rankings in search engine results pages (SERPs). This essay delves into the best practices of Image SEO, offering a comprehensive guide to optimizing visual content for improved search engine performance.
Image SEO is the process of optimizing the images on your website so they are easy for search engines to “read” and find, consequently improving the visibility and rankings of your content in Google and other search engines. Like content image are also show in search and these are more valuable some time over content. So image search engine optimization is a basic term for making the image rank top in the search. For that firstly the google spider need to detect the image by using some basic description. Image SEO is the process of optimizing the images on your website so they are easy for search engines to “read” and find, consequently improving the visibility and rankings of your content in Google and other search engines. Image SEO includes elements like image type, size, and load time and your usage and optimization of alt text and keywords in image file names.
I. Choosing the Right Images
- Relevance to Content: Select images that are directly relevant to the content of the webpage. Images should provide context and support the overall message of the page.
- High-Quality Imagery: Opt for high-resolution images that maintain their clarity even when resized. Crisp and clear images contribute to a positive user experience.
- Originality: Whenever possible, use original images to avoid issues related to copyright and duplication. Unique visuals can also set your content apart from competitors.
II. Image Optimization Techniques
Image optimization refers to the process of creating and delivering high-quality images in the right format, dimension, and resolution for whatever device is accessing them, all while keeping the smallest possible file size.
- File Naming: Choose descriptive file names that accurately reflect the image’s content. Use hyphens to separate words for improved readability, e.g., “mountain-sunset-landscape.jpg.”
- Image Compression: Compress images without compromising quality to reduce file sizes. Smaller file sizes lead to faster page loading times, enhancing user experience.
- Image Format: Select the appropriate format based on the image’s content. Use JPEG for photographs, PNG for images with transparency, and GIF for simple animations.
- Alt Text (Alternative Text): Write informative alt text that describes the image for users who cannot view images, such as visually impaired individuals. Incorporate relevant keywords naturally.
- Image Captions: Include captions to provide additional context for images. Captions offer an opportunity to add relevant keywords and engage users with concise descriptions.
III. Technical Considerations
- Image Dimensions: Scale images to the dimensions they will be displayed at on the webpage. Avoid using oversized images, as they can slow down page loading times.
- Responsive Design: Ensure that images are responsive and adapt to different screen sizes and devices. This is essential for providing a seamless user experience.
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading to defer the loading of images that are not immediately visible on the screen. This speeds up initial page loading times.
IV. Image Sitemaps
Encloses all information about a single image. Each <url> tag can contain up to 1,000 <image:image> tags. <image:loc> The URL of the image. In some cases, the image URL may not be on the same domain as your main site.
- Create an Image Sitemap: Generate a separate XML sitemap for images. This helps search engines discover and index your images more efficiently.
- Include Important Metadata: In the image sitemap, include details such as image location, caption, title, and license information.
V. Social Media and Image SEO
In general, it’s best to stick with PNG, JPG, or WEBP for any images that you upload to your website. The image sharing buttons and open graph tags are in that section.
- Open Graph Tags: Implement Open Graph tags to control how images appear when shared on social media platforms. This ensures that the correct image is displayed with your content.
- Image Sharing Buttons: Integrate social media sharing buttons on your website to encourage users to share your images, expanding your content’s reach.
VI. Monitoring and Optimization
- Regular Review: Periodically review your website’s images to ensure they remain relevant and accurately represent your content.
- Performance Analysis: Use tools to analyze page loading times and image loading performance. Optimize further if any issues arise.
XIII. Structured Data Markup
- Schema Markup: Implement schema markup for images using structured data to provide additional context to search engines. This can enhance how images are displayed in search results, making them more appealing to users.
- Image Objects: Use schema markup to define image objects, including properties like name, description, contentUrl, and author. This helps search engines understand the content and purpose of your images.
XIV. Content Relevance and Context
- Surrounding Text: Ensure that the textual content surrounding your images is relevant and contextually supports the image’s message. This strengthens the overall relevance of the page.
- Keyword Alignment: Align your image optimization strategy with your broader keyword targeting efforts. Use keywords that are relevant to the page’s content and audience.
XV. Reverse Image Search
- Image Ownership: Periodically conduct reverse image searches to check if your images are being used without proper attribution or permission. This helps protect your visual content and maintain your brand integrity.
XVI. Geographic Considerations
- Local Image Optimization: For businesses targeting local audiences, incorporate location-specific keywords and references in image alt text and captions to enhance local search visibility.
- Geo-Tagging: If relevant, consider adding location data (geotags) to your images. This can be particularly useful for businesses in the travel, hospitality, or real estate industries.Check here how website hosting can effects the seo.
XVII. Monitoring and Analysis
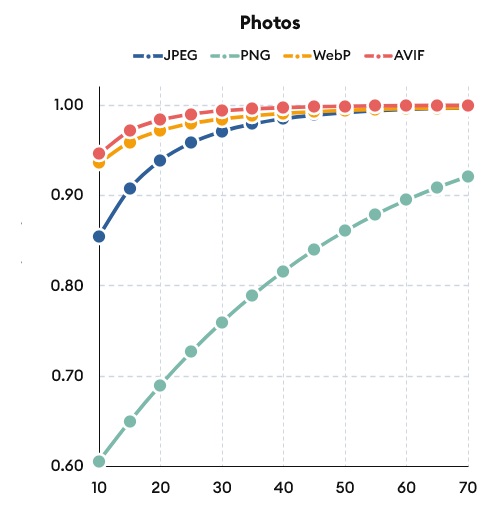
- Google Search Console: Monitor the performance of your images using Google Search Console. Track impressions, clicks, and positions to assess the impact of your Image SEO efforts.
- Image Search Traffic: Analyze website traffic from image searches to identify which images are driving the most engagement and conversions. Use this information to refine your image optimization strategy.
XVIII. Social Proof and User-Generated Content
- Reviews and Testimonials: Utilize images shared by customers in reviews and testimonials. Authentic user-generated content can enhance credibility and contribute to a positive online reputation.
- UGC Guidelines: When using user-generated images, ensure that you have the necessary rights to do so and adhere to any guidelines or permissions provided by the content creators.
XIX. Video Thumbnails Optimization
- Video Thumbnails: If your website includes videos, optimize video thumbnails for search engines. Use high-quality images that accurately represent the video’s content.
- Video Rich Snippets: Implement video schema markup to enhance the visibility of video thumbnails in search results. This can lead to higher click-through rates and increased traffic.
XX. Image CDN (Content Delivery Network)
An image CDN is a regular content delivery network topped with a set of software enhancements to enhance the underlying CDNs functionality for optimizing and transforming images in real-time, thereby making it more suitable for image delivery.
- CDN Integration: Utilize a specialized CDN for images to distribute your visual content across multiple servers worldwide. This reduces latency, enhances loading speeds, and ensures consistent delivery.
- Image Optimization Plugins: Leverage CDN-integrated optimization plugins that automatically resize, compress, and cache images, optimizing performance and user experience.
XXI. WebP and Next-Gen Formats
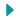
Next-gen formats such as WebP or AVIF provide superior compression features compared to all the other web image formats. These both format prevent from downloading and repllicating the image which means it help to not only give high compression even it help to protect piracy.
- WebP Format: Consider using the WebP image format, which provides higher compression rates while maintaining image quality. This format can significantly improve loading times.
- AVIF Format: Experiment with AVIF, a newer image format that offers even better compression and quality preservation. Keep in mind that browser support may vary.
XXII. Visual Search Optimization
This allows search engines to better understand the content of visual media and provide more relevant and accurate results to users. One example of visual search optimization in action is when a user performs a search on a search engine using an image rather than a text-based query.
- Visual Search Engines: Optimize your images for visual search engines and platforms. Use unique, eye-catching images and proper metadata to increase the chances of your content being discovered.
- Reverse Image SEO: Optimize images for reverse image searches. Use descriptive filenames, alt text, and captions to make your images more discoverable through reverse image searches.
XXIII. Image Experiments and Analysis
Ab testing and heatmap analysis take the vital role in that section.Image analysis involves processing an image into fundamental components to extract meaningful information. Image analysis can include tasks such as finding shapes, detecting edges, removing noise, counting objects, and calculating statistics for texture analysis or image quality.
- A/B Image Testing: Continuously experiment with different images for the same content and measure their impact on user engagement, conversions, and overall site performance.
- Heatmaps and Analytics: Utilize heatmaps and advanced analytics tools to understand how users interact with your images. This insight can guide further optimization strategies.
XXIV. Internationalization and Multilingual SEO
Though that is difficult to handle yet if that can be done then that can bring best output. Multilingual SEO is a set of best practices that can help your site rank high in search engines in different languages. Get to know them all. The internet has created a big playing field for businesses—one where the competition is global.
- Multilingual Alt Text: If your website caters to different languages, ensure that alt text and metadata are translated to accurately represent the image’s content in various languages.
- Cultural Sensitivity: When targeting international audiences, be culturally sensitive with image choices and avoid using visuals that might be misunderstood or offensive in certain regions.
XXV. Image SEO Audits and Updates
An Image SEO audit is the process of evaluating how well your website is optimized for search engines. It identifies errors that can prevent your site from ranking well and opportunities that can help you rank better. An SEO audit usually covers areas like: Indexing and crawlability.
- Regular Audits: Conduct comprehensive image SEO audits periodically to identify any outdated or poorly performing images. Replace or update images as needed to maintain relevance.
- Image File Names: Keep image file names consistent with the latest SEO trends and keyword strategies. Renaming images can help align them with evolving search trends.
Image SEO is a multidimensional strategy that requires attention to detail, continuous monitoring, and a commitment to user satisfaction. By implementing these diverse best practices, you can position your website’s visual content to effectively attract search engine attention, engage users, and drive organic traffic. Remember that Image SEO is an ongoing process, and adapting to algorithm changes, user behavior shifts, and industry trends will ensure that your images remain a valuable asset in your digital marketing toolkit.As your expertise in Image SEO deepens, incorporating these advanced best practices can provide a competitive edge in the digital landscape. Continuously exploring new optimization techniques, staying updated with industry trends, and adapting to algorithm changes will allow you to extract maximum value from your visual content. By elevating your image optimization strategies to an advanced level, you can pave the way for enhanced search visibility, increased user engagement, and sustained online success.